For data-driven marketing, it's essential to get customer data of the highest quality possible.
The traditional tracking method – client-side tracking – does not provide that anymore as ad blockers and in-browser third-party cookie restrictions keep developing.
Server-side tracking is coming to become a new industry standard, providing accurate and complete data while ensuring better security and protection.
Let's see how both methods work and why one of them is overtaking the other.
The two ways of tracking in analytics
There are two ways to track users' actions on your website. The difference is in the way the data is transferred from a user's browser to the chosen analytics tools.
Client-side tracking is the standard right now – analysts and marketers have been using it for years now. It implies transferring the data directly from the users' browser directly to an external platform like Google Analytics.
Server-side tracking is a reliable method in which data from a user's browser first collects in a company's web server first, and only then distributes by external services. This is a more secure approach and also provides better quality data.
What's wrong with client-side tracking?
Ad blocker extensions and browser restrictions, like Safari's intelligent tracking prevention (ITP), are developing and making tracking users' actions more difficult. While it's a good thing in terms of security, this also means that the data you receive is significantly incomplete.
Because both ad-blocking systems and browser restrictions work by blocking or cutting down third-party cookies, the data collected with client-side tracking comes to the analyst incomplete and often misleading.
The question is, how many of your customers use ad blockers or browsers that restrict third-party cookies? Well.
According to a study by Hootsuite, 37.5% of internet users in the world block online ads with an ad-blocking extension. That means that because of these extensions, you're potentially getting low-quality or no data from more than ⅓ of your website visitors.
Aside from that, all Safari users fall under the category of people whose actions you can't properly track. In the US, that is over half of all mobile phone users (54%). Soon enough, all Chrome users will also be in this category when Google finishes block third-party cookies by 2024.
How it affects your data analytics stack
When you can't properly track your users' actions, you get poor and incomplete data, which leads to misled marketing moves, and, essentially, costs you money.
In total, businesses lose $15 million a year due to poor data quality, according to Gartner's Data Quality Market Survey in 2017. As you can imagine, with more cookie restrictions coming this figure will only grow.
If you are still using client-side tracking, you cannot get a full picture of how many users visit your website, how they interact with it, or which of your advertisement channels are working better.
The false illusion of an increase in direct traffic and misled decisions in advertising campaign optimization
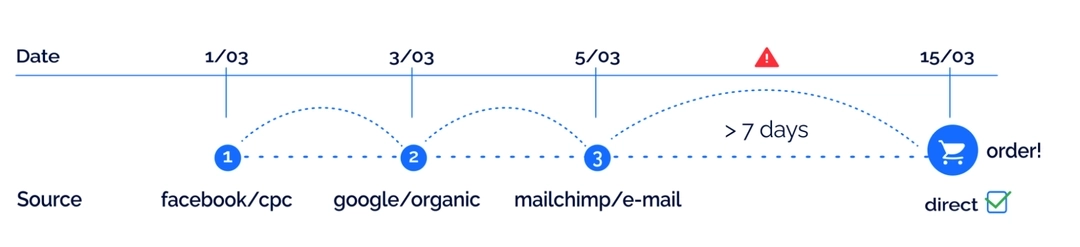
Because of the ITP, a Safari user that entered your website from an advertising channel and then revisited your website in more than a week will be identified as a new user from a direct source. The more Safari users you have, the more misled you will be by the analytics reports.
Miscalculated ROAS in attribution models
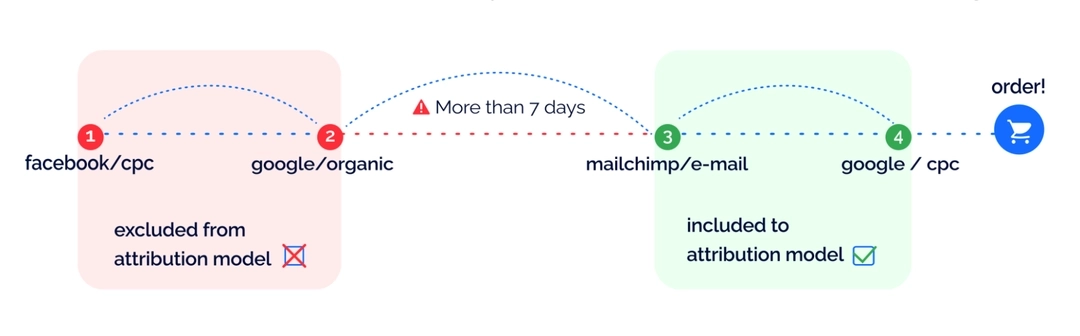
Because of the incomplete data, the attribution models are inaccurate. This can lead to poor decisions in budgeting and building the advertising channel chain.
Inaccurate retention reports
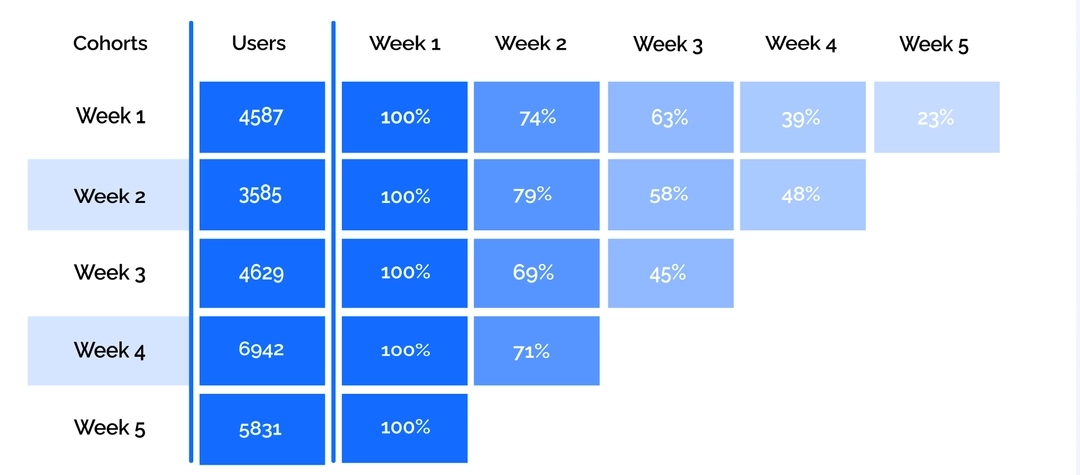
Because of the identification issues, you can notice weaker cohorts in your retention reports. This can lead to wrong conclusions on customer outflow. Find more detailed information on the effect of cookies restrictions in our article.
Now let's dive deeper into the tech stuff and see how data quality can easily be improved with the use of server-side tracking.
What is client-side tracking?
With client-side tracking, data is transferred directly from a user's browser to an external server, such as Google Analytics or Facebook Pixel. The data transfer is enabled by small pieces of JavaScript code – tracking scripts.
Here's how the tracking happens. Analytics tools use cookies to identify users, track their actions and create reports using that data. The cookie request is sent from the analytics instance to the client's browser. Cookies then are used by the analytics platform to identify the user.
When a third-party analytics platform sends a cookie request, ad blockers and tracking protection systems like ITP recognize these cookies as third-party, which means that they can block or impact them.
Client-side tracking does not allow control over which data is sent to the analytics instance. It also slows down the page speed and is not the most secure option.
Still, there are some things that attract marketers to client-side tracking. For instance, if you're using a tag management system like Google Tag Manager, it's very easy to set up and does not require advanced tech skills.
What is server-side tracking?
The server-side tracking method implies collecting data first on your web server and only then sending it to a data processing platform, like Facebook Pixel.
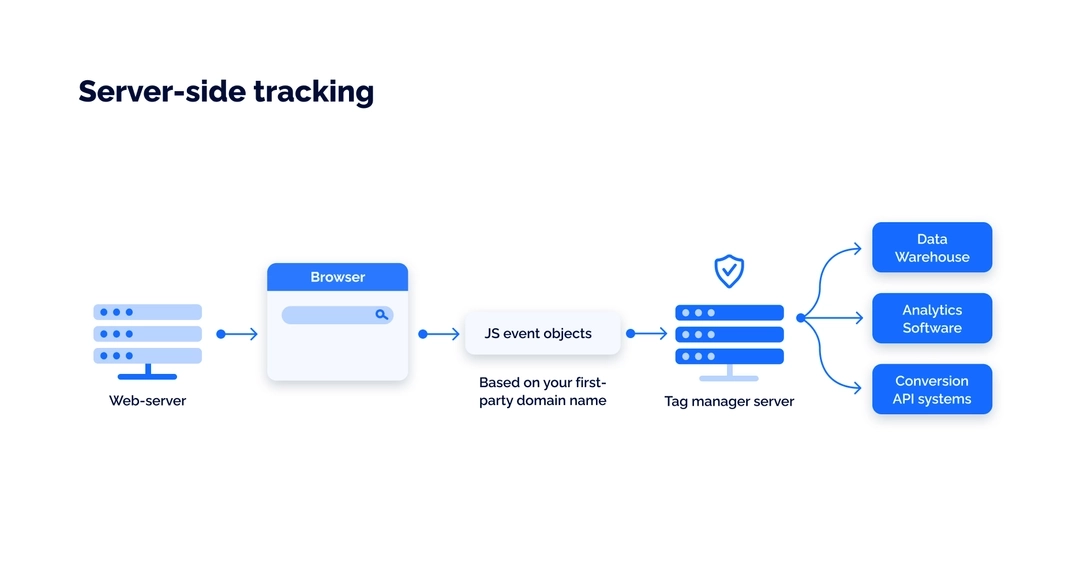
With server-side integration, the cookie request is sent from the server that hosts your website, and these cookies are identified as first-party. Ad blocks and ITP cannot impact first-party cookies, so you can ensure higher accuracy and completeness of customer data.
The data received by the server can later be organized, sorted, and sent to third-party analytics tools.
Server-side tracking provides more complete data. Aside from that, it allows for better control over data and better security. Another important thing is it ensures that your data collection process meets the requirements of privacy regulations like GDPR.
The downside of this method is that it's not that easy to install and will very likely require developers support. On the other hand, there are tools that make it accessible to non-developers.
Difference between client-side and server-side tracking
As side-by-side comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of both tracking methods:
| Feature | Client-side Tracking | Server-side Tracking |
|---|---|---|
| Data Quality | Low (affected by ad blockers & ITP) | High (bypasses ad blockers) |
| Cookie Type | Third-party cookies | First-party cookies |
| Privacy Compliance | Limited control | Full control |
| Page Speed | Slower (multiple scripts) | Faster (server processing) |
| Data Security | Less secure | More secure |
| Setup Complexity | Easy | More complex |
| Developer Support | Not required | Often required |
| Data Control | Limited | Full control |
How does server-side tracking work?
With server-side tracking, the data is processed and filtered on your server, which means it will not affect the loading speed for customers. Collected data then can be sent to any platform you use.
The tracking code sends a request from a user's browser to your server — the same one that hosts your website. Then that data is processed and sent to any destination you use. This could be an analytics tool, a data warehouse, a CRM, or any other service.
The exciting thing about this is that you can control which data to send to which third-party instance. The not-so-exciting part is that often the process is not that easy to set up.
For instance, when you work with common tag managers, like Google Tag Manager Server-Side, you need to get very technical and deploy the servers and configure them by yourself. This cannot be done without developer support.
Does this mean you can't implement server-side tagging without a developer? Not really. You just need to be more careful with your selection of tools. For example, Renta's JavaScript SDK allows for quick integration without much tech knowledge.
With Renta's JavaScript SDK, you can set up data streaming to your warehouse and create a real-time integration of collected data with your third-party destinations. For instance, you can set up data streaming to Facebook Conversion API in a matter of minutes.
Finally, server-side tagging could improve your website's loading speed. When the data processing happens in a separate container in the cloud, it lightens your website, and users' requests process quicker.
So, let's sum this up. The key benefits of server-side tagging are:
- fuller and more accurate data, which allows you to make informed marketing decisions and up your advertising game;
- better protection of data and more control over it at each step of collection and distribution processes;
- improved page speed due to the reduced workload on the user's browser;
- compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA through better data control.
Server-side analytics tools
There are several tools that allow you to implement server-side tracking:
- Google Tag Manager Server-Side - requires technical setup and server deployment
- Segment - a customer data platform with server-side capabilities
- Renta - an easy-to-use solution with quick setup and no-code integrations
- Snowplow - an open-source event data collection platform
- mParticle - a customer data platform for mobile and web
Each tool has its own advantages, but the key is to choose one that fits your technical capabilities and business needs.
Key takeaways on server-side tracking
Server-side tracking is becoming the industry standard for good reasons:
- It provides more accurate and complete data by bypassing ad blockers and browser restrictions
- It offers better security and privacy compliance through first-party cookies and controlled data flow
- It improves website performance by reducing the load on users' browsers
- It gives marketers full control over what data is collected and where it's sent
While the setup might be more complex than client-side tracking, the benefits far outweigh the initial investment. With tools like Renta, even non-technical teams can implement server-side tracking and start benefiting from higher quality data.
If you're still relying on client-side tracking, now is the time to make the switch. Your marketing decisions depend on accurate data, and server-side tracking is the best way to ensure you're getting it.
How to implement server-side tracking with Renta
Quick start guide: Setting up server-side tracking
Visit Renta.im and sign up for a free account. No credit card required to get started.
Add the Renta tracking script to your website. You can either install it via npm or use our CDN snippet:
npm install @renta/trackerOr include the script directly in your HTML:
<script src="https://cdn.renta.im/tracker.js"></script>In the Renta dashboard, set up your data sources. This tells Renta which events to track and how to structure your data.
Link your analytics tools, data warehouses, and marketing platforms. Renta supports Google Analytics, Facebook Pixel, Snowflake, and many more.

Use Renta's testing tools to verify your setup, then deploy to production. Your first-party data collection is now live!